Monkeypox is on the rise in many countries, causing concern, particularly with reported cases in Vietnam. So, what are the symptoms of monkeypox? What measures should be taken if there is suspicion of infection, and how can one prevent it? Let’s explore these questions in the following article!
What is Monkeypox?
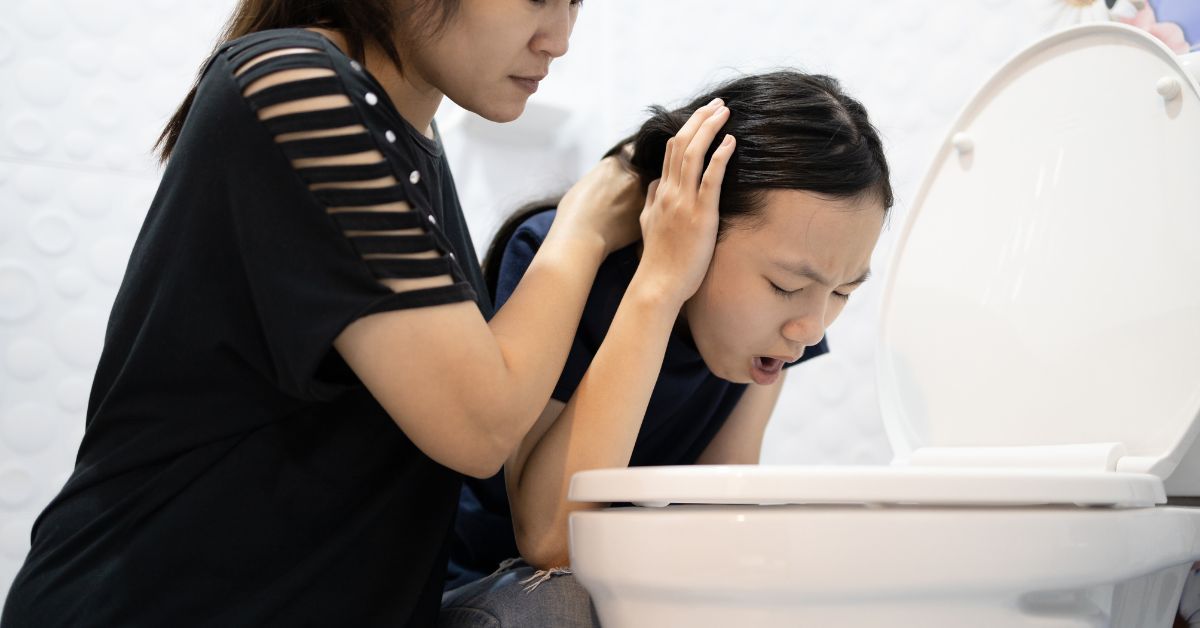
Monkeypox is an infectious disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which can be transmitted from animals to humans and, in turn, from person to person. It presents with various signs and symptoms, with some individuals experiencing mild symptoms while others may develop severe symptoms requiring medical attention.
Monkeypox is currently on the rise in Vietnam
High-Risk Groups for Monkeypox
Certain groups are at a higher risk of contracting monkeypox, including:
1. Pregnant women
Due to their weakened immune systems, pregnant women are at a higher risk of contracting monkeypox.
2. Children
The underdeveloped immune systems of children make them more susceptible to infection and severe symptoms.
3. Immunocompromised individuals
Those with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy or having immune-related disorders, are at an increased risk of infection and severe symptoms.
4. Healthcare workers
Individuals working in the healthcare sector, especially those in direct contact with monkeypox patients, face a higher risk of infection.
5. Close contacts with infected individuals or animals
Anyone in close contact with a person with monkeypox, including sexual partners or those frequently exposed to infected animals, is at an elevated risk.
Symptoms of Monkeypox
Monkeypox can manifest various symptoms, and the severity depends on the individual and the extent of the infection. Common symptoms of monkeypox include:
- Fever: High body temperature is a common symptom.
- Headache: Intense and discomforting headaches may occur.
- Muscle and back pain: Aching sensations in muscles and the back are common.
- Body weakness: Feeling tired, fatigued, and weak.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Enlargement of lymph nodes, typically in the neck, armpits, and groin areas.
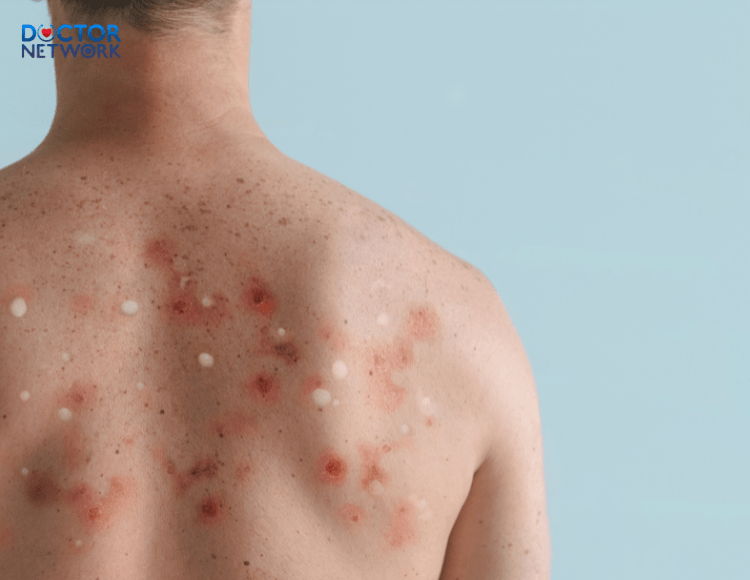
- Skin rash: A distinctive symptoms of monkeypox, initially appearing as flat spots on the face, palms, soles, eyes, mouth, genitals, anus, and surrounding areas.
- Progression of the rash: Initially flat, the spots may develop into fluid-filled blisters, pustules, dry up, and eventually peel off, revealing new skin underneath.
Is Monkeypox Dangerous?
Monkeypox can pose a significant threat to certain groups, especially children, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems. In severe cases, complications such as encephalitis, myelitis, and endocrine complications can occur, requiring careful medical attention.
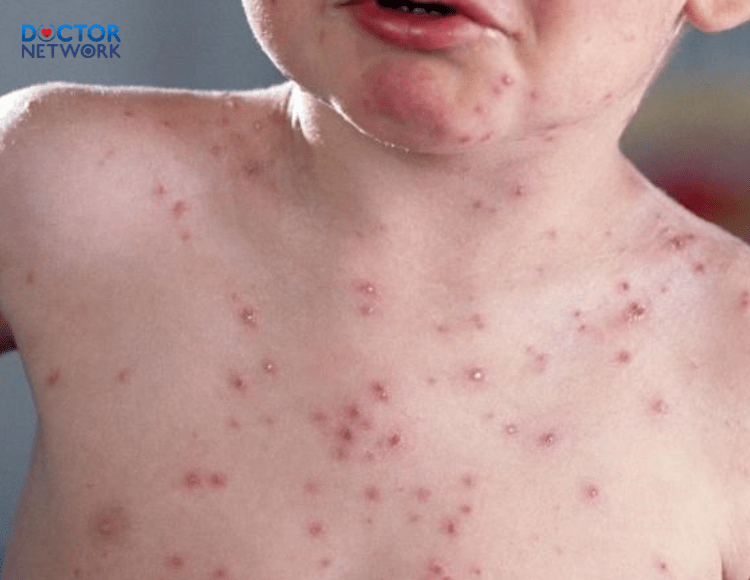
Children are at high risk of contracting monkeypox and may be prone to fatal outcomes
Treatment of Monkeypox
Currently, there is no specific treatment or antiviral medication for monkeypox. The focus is on supportive care to alleviate symptoms and help the body combat the infection. This includes:
- Rest and healthcare: Adequate rest and maintaining good health are crucial. Stay hydrated, follow a balanced diet, and ensure sufficient sleep to support the body’s recovery.
- Fever and pain management: Use pain relievers and fever-reducing medications as directed by a healthcare professional.
- Skin care: Keep the skin clean and dry. Use moisturizers or anti-itch medications if necessary.
- Professional medical care: If you suspect you have monkeypox or experience symptoms, especially if you are at a higher risk, seek medical attention promptly for diagnosis and professional care.

Vaccination is an effective preventive measure against the disease
Preventive Measures for Monkeypox
Several preventive measures can help reduce the risk of contracting monkeypox:
- Vaccination: If a monkeypox vaccine is available, getting vaccinated is the most effective preventive measure.
- Personal hygiene: Wash hands regularly with soap and clean water, especially after contact with infected individuals or animals, before eating, and after using the restroom.
- Avoid close contact with infected individuals: Minimize close contact with people with monkeypox to reduce the risk of transmission. Be cautious when caring for and interacting with patients, particularly those showing symptoms.
- Environmental hygiene: Ensure cleanliness in living and working environments, focusing on personal belongings, and the surrounding areas.
- Adhere to safety measures when in contact with animals: Avoid close contact with wild animals or those raised as pets.
- Avoid close contact with outbreak areas: If there are reports of an outbreak, limit travel and close contact with that region.
- Supporting Immune Health: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep, can enhance immune function and contribute to overall well-being.
While the article has provided information on “Symptoms of monkeypox“, it is crucial to remember that adherence to personal hygiene measures and avoiding sources of infection can help reduce the risk of contracting monkeypox. If any “Symptoms of monkeypox” are observed, seek prompt medical attention for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.