Glands are specialized organs responsible for synthesizing and secreting substances that serve various functions within the body. The two main types, endocrine and exocrine glands, work in coordination but have fundamental differences that impact many aspects of health. Let’s delve into how to “Distinctions Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands” in this article.
Distinctions Between Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
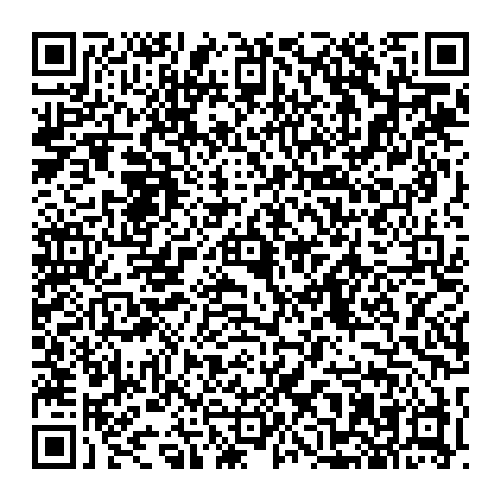
Endocrine Glands: These glands lack ducts. Their secretions, known as endocrine hormones, are released directly into the bloodstream, traveling to target organs throughout the body to regulate numerous vital processes.
“distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands” – Endocrine glands: Are glands without ducts
Exocrine Glands: These glands possess ducts that carry their secretions (such as sweat, digestive juices, tears, etc.) to the body’s surface or into body cavities, serving specific functions.
Understanding the roles and distinctions between endocrine and exocrine glands helps us appreciate their importance in maintaining the body’s smooth operation.
Differentiating Endocrine and Exocrine Glands
Key differences between endocrine and exocrine glands include:
- Secretions: Hormones (endocrine) vs. sweat, digestive juices, saliva, sebum, etc. (exocrine)
- Transportation Route: Directly into the bloodstream (endocrine) vs. through ducts (exocrine)
- Target Organs: Distant organs and tissues (endocrine) vs. body surface or cavities (exocrine)
- Examples: Thyroid gland, pancreas, pituitary gland (endocrine) vs. sweat glands, salivary glands, sebaceous glands (exocrine)

“distinguish endocrine and exocrine glands” – such as sweat, digestive juices, tears
Functions and Roles
Endocrine Glands:
- Regulate bodily processes: growth, metabolism, reproduction, internal balance, etc.
- Control mood, sleep, appetite, etc.
Exocrine Glands:
- Protect and lubricate body surfaces.
- Aid in digestion and excretion.
- Regulate body temperature (sweat glands)
Endocrine and Exocrine Systems
These two systems work closely together to ensure efficient bodily function. The endocrine system has a broader influence due to hormones’ systemic effects. Endocrine regulation occurs through feedback mechanisms, ensuring hormone levels remain within appropriate ranges.
Common Disorders
- Endocrine Disorders: Diabetes, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, adrenal gland disorders, etc.
- Exocrine Disorders: Cystic fibrosis, dry eye, pancreatitis, etc.
Maintaining Endocrine and Exocrine Health
- Balanced Diet: Provide adequate nutrients to support gland function.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, stress management, sufficient sleep.
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection and timely treatment of abnormalities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the primary roles of endocrine and exocrine glands?
Endocrine glands: Their main function is to produce and release hormones into the bloodstream. These hormones travel to target organs throughout the body, binding to receptors to transmit signals and regulate essential physiological activities, such as:
- Metabolism: Insulin and glucagon regulate blood sugar levels; thyroid hormones control basal metabolic rate.
- Growth and development: Growth hormone (GH) stimulates the growth of height, bones, and muscles; thyroid hormones contribute to intellectual and nervous system development.
- Reproduction: Male (testosterone) and female (estrogen, progesterone) sex hormones regulate reproductive functions and develop secondary sexual characteristics.
- Homeostasis: The adrenal hormone system (cortisol, aldosterone) helps the body adapt to stress, maintain blood pressure, and balance electrolytes.

“distinguish endocrine and exocrine glands” – endocrine glands produce and secrete hormones
Exocrine glands: Their main function is to produce and secrete substances directly onto the body’s surface or into body cavities. The secretions of exocrine glands play roles in:
- Protection: Sweat helps regulate body temperature and excrete toxins; saliva and tears moisten and protect the eyes.
- Lubrication: Sebum lubricates joints and skin; saliva helps lubricate food during chewing and swallowing.
- Digestion: Gastric juice contains enzymes that digest protein; pancreatic juice contains enzymes that digest carbohydrates and fats.
- What are some examples of endocrine and exocrine glands?
- Endocrine glands: Thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, pancreas (endocrine part), gonads (ovaries, testes),adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
- Exocrine glands: Sweat glands, salivary glands, lacrimal glands, sebaceous glands, mammary glands, pancreas (exocrine part).
How can we differentiate between endocrine and exocrine glands?
The key difference between endocrine and exocrine glands lies in how they secrete their products and how these products affect the body:
Endocrine glands:
- Secretions: Hormones
- Secretion method: Ductless, hormones are secreted directly into the bloodstream.
- Mode of action: Hormones travel to target organs throughout the body, bind to receptors, and regulate physiological activities.
Exocrine glands:
- Secretions: Sweat, digestive juices, saliva, sebum, etc.
- Secretion method: Ducts carry secretions to the body’s surface or into body cavities.
- Mode of action: Secretions usually act locally, at the site of secretion.
What are the potential consequences of endocrine and exocrine gland disorders?
Dysfunction of endocrine and exocrine glands can lead to various serious health problems, including:
- Metabolic disorders: Diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia.
- Growth and development disorders: Short stature, precocious puberty, delayed development.
- Reproductive disorders: Infertility, subfertility, menstrual irregularities.
- Mood disorders: Depression, anxiety, sleep disorders.
- Muscle weakness and fatigue: Hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency.
- Skin conditions: Dermatitis, acne, hair loss.
- Digestive disorders: Pancreatitis, gallstones.
How can we maintain the health of our endocrine and exocrine systems?
To maintain the health of your endocrine and exocrine systems, you should:
- Maintain a balanced diet: Provide adequate essential nutrients.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Exercise regularly, manage stress, get enough sleep.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption: These habits can negatively impact both endocrine and exocrine gland function.
- Get regular check-ups: Early detection and treatment of any abnormalities can prevent serious health complications.
Scientific Evidence
- Anatomy and Physiology Textbooks: Describe the structural and functional differences between endocrine and exocrine glands.
- Scientific Articles: Discuss the roles of specific hormones and exocrine secretions in various physiological processes.
- Medical Reviews: Summarize current knowledge on endocrine and exocrine disorders, their diagnosis, and treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between endocrine and exocrine glands helps us appreciate their roles in maintaining overall health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and seeking timely medical care, we can promote the well-being of these vital systems.
References:
https://study.com/learn/lesson/exocrine-endocrine-glands.html
https://byjus.com/question-answer/what-are-the-differences-between-endocrine-system-and-exocrine-system/
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-endocrine-and-exocrine-glands/
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.