Hemorrhoids typically resolve within a few days to several weeks, depending on their type, severity, and underlying causes. These swollen, enlarged veins in the rectum and anus affect millions of people worldwide, causing uncomfortable symptoms like pain, itching, bleeding, and swelling that can significantly impact daily activities including sitting, walking, and bowel movements.
“How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?” – This comprehensive medical guide covers everything you need to know about hemorrhoid duration, from acute flare-ups to chronic conditions. We’ll explore the different types of hemorrhoids, factors affecting healing time, effective treatment options, prevention strategies, and when to seek professional medical care. Understanding these aspects helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment and recovery timeline.
What Exactly Are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are naturally occurring vascular structures consisting of swollen, enlarged veins located in the anus and rectum that become problematic when they swell beyond normal size. Every person is born with these vascular cushions, but issues arise when increased pressure causes them to become inflamed, enlarged, or displaced from their normal position.
These common anorectal conditions affect approximately 5% of Americans annually and more than half of all individuals over age 50. The prevalence increases with age due to weakening connective tissues and decreased muscle tone in the pelvic floor region.
Types of Hemorrhoids
Internal Hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum above the dentate line and are typically painless because this area lacks pain-sensitive nerve endings. These hemorrhoids may cause bleeding during bowel movements but usually aren’t felt unless they prolapse or extend outside the anal opening.
External Hemorrhoids form under the skin around the anus below the dentate line and can be extremely painful, itchy, and tender due to the abundant nerve supply in this region. These hemorrhoids appear as skin-colored, soft lumps that can often be seen or felt during examination.
Prolapsed Hemorrhoids occur when internal hemorrhoids bulge outside the anus, potentially causing bleeding, pain, and discomfort. Depending on severity, some prolapsed hemorrhoids can be gently pushed back inside manually.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids develop when blood clots form within external or internal hemorrhoids, creating firm, purple, blue, or black lumps outside the anus. These represent the most painful type of hemorrhoid and require immediate medical attention for optimal outcomes.

The Core Question: How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?
There is no universal timeframe for hemorrhoid resolution, as duration varies significantly based on multiple factors including type, severity, treatment approach, and individual patient characteristics. Small, uncomplicated hemorrhoids often clear up without intervention within just a few days, while more severe cases may persist for weeks or months without proper treatment.
Duration by Hemorrhoid Type
| Hemorrhoid Type | Typical Duration | Treatment Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Small External | 3-7 days | Often resolves naturally |
| Internal (Grade 1-2) | 1-2 weeks | Home care usually sufficient |
| Prolapsed | 2-4 weeks | May require medical intervention |
| Thrombosed | 2-3 weeks | Often needs professional treatment |
| Large/Severe | Weeks to months | Usually requires medical procedures |
External Hemorrhoids typically last several days to one week, though duration may extend longer depending on size and aggravating factors such as excessive wiping, prolonged sitting, or continued straining during bowel movements. Most external hemorrhoids resolve eventually without medical treatment.
Internal Hemorrhoids show variable duration patterns. Asymptomatic internal hemorrhoids may remain unnoticed indefinitely, while symptomatic ones causing bleeding, itching, discomfort, or prolapse may persist for several weeks or longer. Some internal hemorrhoids develop into chronic conditions requiring medical intervention.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoids can last two to three weeks or longer, with blood clots potentially diminishing within a couple of weeks. However, the underlying hemorrhoid structure doesn’t necessarily disappear even after clot resolution.
With consistent home care treatment, hemorrhoid symptoms like pain and bleeding typically improve within one week, though complete resolution may take slightly longer depending on individual healing capacity.
Factors That Affect Hemorrhoid Duration and Healing
The severity of hemorrhoidal disease significantly influences healing time, with larger or more advanced hemorrhoids (higher grade classifications) more likely to persist and require professional treatment. Grade 1 hemorrhoids demonstrate the highest likelihood of spontaneous resolution without intervention.
Underlying Causes and Risk Factors
Resolving underlying causes often proves essential for eliminating hemorrhoids permanently. The primary mechanism involves excessive pressure on veins in the anorectal region, commonly caused by:
- Straining during bowel movements (Valsalva maneuver)
- Prolonged toilet sitting with reading or mobile device use
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea episodes
- Insufficient dietary fiber intake
- Inadequate fluid consumption
- Sedentary lifestyle with minimal physical activity
Risk factors that prolong healing and complicate recovery include:
- Dietary Factors: Low-fiber diets, processed food consumption, inadequate hydration
- Physical Factors: Obesity, pregnancy, aging muscle tone, anal intercourse
- Behavioral Factors: Overuse of laxatives or enemas, delayed bowel movement response
- Medical Conditions: Chronic constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, liver disease
Lifestyle Habits That Promote Faster Healing
Adopting a high-fiber diet with 25-38 grams daily from fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains significantly accelerates healing by producing softer stools that reduce straining. Adequate hydration through increased water consumption and regular physical activity promote healthy bowel function and improved circulation.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids: What to Look For
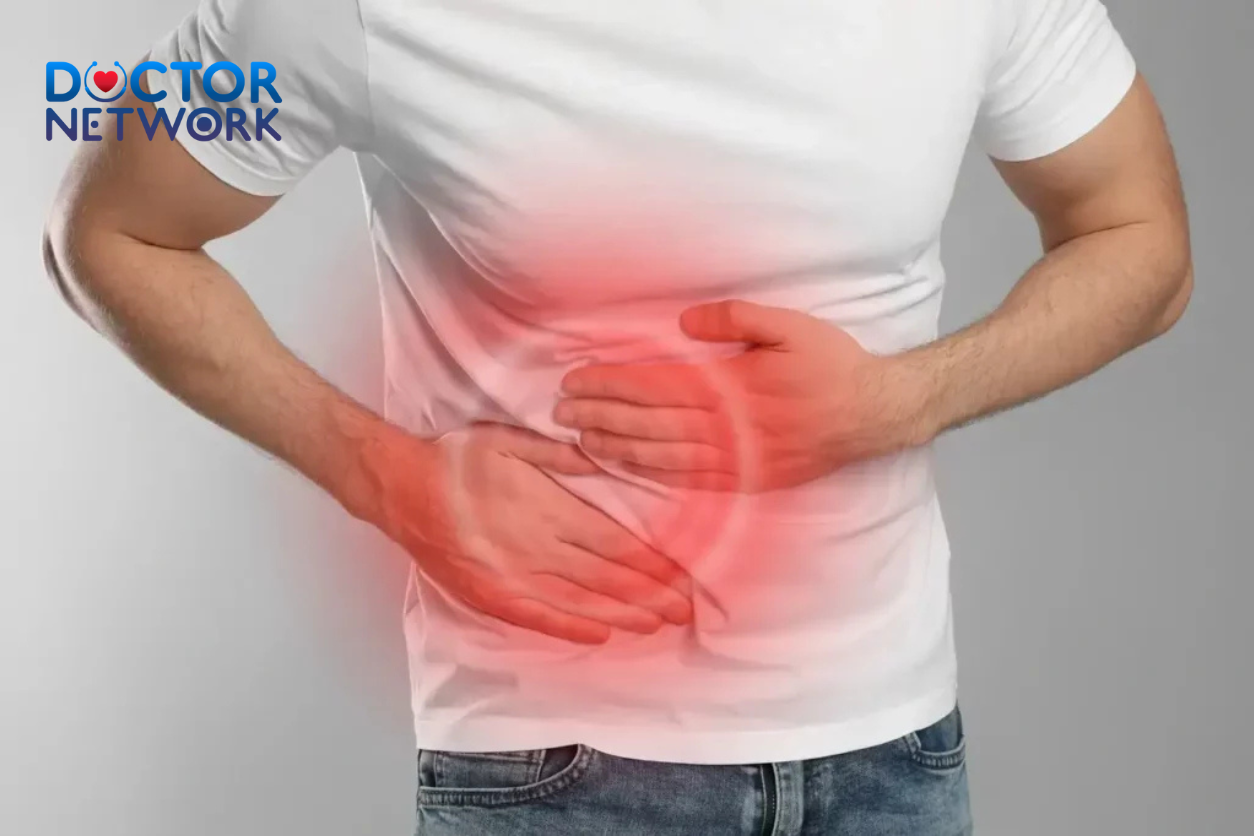
Recognizing hemorrhoid symptoms enables early intervention and prevents progression to more severe stages requiring intensive medical treatment. Common manifestations include itchiness or irritation around the anal area, particularly after bowel movements or prolonged sitting.
Primary Symptoms Include:
- Pain or aching sensation in the anus, especially when sitting
- Hard, sore, or tender lumps near the anus (external hemorrhoids)
- Bright red bleeding when wiping or visible in toilet water
- Swelling and inflammation around the anal opening
- Pain during bowel movements or immediately afterward
Internal hemorrhoids rarely cause pain unless they prolapse beyond the anal opening, as the rectum lacks pain-sensitive nerve fibers. However, they commonly cause painless bleeding that appears as bright red blood on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Thrombosed Hemorrhoid Symptoms: Thrombosed hemorrhoids cause characteristically severe and sudden pain, significant swelling, and intense inflammation that may interfere with normal activities. Intense pain and bleeding can occur if a thrombosed hemorrhoid ruptures, creating a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
When Symptoms Persist: Knowing When to See a Doctor
Hemorrhoids that don’t improve within one to two weeks of consistent at-home treatment warrant professional medical evaluation. Symptoms that worsen or significantly interfere with daily activities, work performance, or sleep quality indicate the need for specialized care.
Critical Warning Signs
Blood in Stool: Always consult a healthcare provider when experiencing rectal bleeding, even if hemorrhoids seem likely. Bright red blood typically indicates direct irritation from hemorrhoids and should resolve with proper healing. However, darker blood may signal problems higher in the digestive tract requiring different treatment approaches.
Severe Pain: Sudden, intense pain suggests thrombosed hemorrhoids or other complications requiring immediate medical attention. Severe rectal bleeding represents a serious medical sign that demands urgent evaluation.
Signs of Infection: Intense swelling, fever, chills, or discharge around the anal area may indicate bacterial infection requiring antibiotic treatment.
Additional Concerning Symptoms:
- Persistent abdominal pain
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
- Changes in bowel habits
Importance of Professional Diagnosis
Hemorrhoid symptoms frequently overlap with other serious anorectal conditions including anal fissures, colorectal polyps, and anal cancer. Healthcare providers can provide accurate diagnoses through comprehensive symptom evaluation and physical examination, potentially including digital rectal examination, anoscopy, or sigmoidoscopy.
Professional diagnosis becomes particularly important for individuals over 50 years old, as the risk of colorectal cancer increases with age. Don’t allow embarrassment or fear to prevent seeking appropriate medical care when symptoms persist or worsen.
Managing Symptoms and Promoting Healing
Smaller hemorrhoids often respond successfully to conservative home treatment approaches that focus on symptom relief and promoting natural healing processes. Effective home management combines lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and over-the-counter treatments.
Lifestyle and Behavioral Modifications
Proper Toilet Habits:
- Respond promptly to bowel movement urges without delay
- Elevate legs on a footstool while using the restroom to optimize anal canal position
- Limit toilet sitting time and remove distractions like phones or reading materials
- Avoid excessive straining or pushing during bowel movements
Hygiene and Comfort Measures:
- Shower regularly and wash the anal area gently after each bowel movement
- Use plain water, moistened wipes, or soft toilet paper for cleaning
- Take warm sitz baths for 10-20 minutes daily to relieve symptoms and enhance blood circulation
- Apply ice packs or cold compresses to reduce pain and swelling
- Use donut cushions to reduce pressure when sitting for extended periods
Dietary and Hydration Strategies
Fiber Intake Optimization: Increasing dietary fiber to 25-38 grams daily through natural sources significantly improves stool consistency and reduces straining. Excellent fiber sources include:
- Fresh fruits: apples, pears, berries, oranges
- Vegetables: broccoli, Brussels sprouts, artichokes, sweet potatoes
- Whole grains: oats, quinoa, brown rice, whole wheat bread
- Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas, split peas
Fiber Supplements: Consider methylcellulose (Citrucel) or psyllium husk (Metamucil) when dietary fiber intake proves insufficient. Start with small doses and increase gradually to prevent gas and bloating.
Hydration Requirements: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain soft stool consistency and prevent constipation. Aim for 8-10 glasses of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate conditions.
Over-the-Counter and Prescription Medications
| Medication Type | Active Ingredients | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Creams | Lidocaine, Hydrocortisone | Pain relief, inflammation reduction |
| Suppositories | Witch hazel, Phenylephrine | Swelling reduction, symptom relief |
| Oral Pain Relievers | Ibuprofen, Acetaminophen | Pain management, inflammation control |
| Stool Softeners | Docusate sodium | Easier bowel movements |
Topical Treatments including creams, ointments, gels, and suppositories containing lidocaine provide local anesthetic effects, while witch hazel offers astringent properties that reduce swelling. Hydrocortisone preparations help control inflammation, and zinc oxide specifically addresses itching symptoms.
Oral Medications such as ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and aspirin provide systemic pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects. Use stool softeners or mild laxatives only as recommended by healthcare providers to avoid dependency.
Prescription Options may include stronger corticosteroid preparations, lidocaine with tribenoside combinations, or phlebotonic drugs that strengthen vein walls. Long-term corticosteroid use carries risks of skin thinning and other side effects.
Medical Treatment Options
Persistent, recurrent, or severe hemorrhoids may require professional medical intervention when conservative home treatments prove insufficient. Treatment selection depends on hemorrhoid type, severity grade, patient symptoms, and individual medical history.
Non-Surgical Procedures
Most outpatient procedures can be performed in clinic settings with minimal or no anesthesia, offering effective treatment with reduced recovery time compared to surgical options.
Rubber Band Ligation involves placing small elastic bands around internal hemorrhoid bases to cut off blood supply. The hemorrhoid tissue dies and falls off within one week. This procedure may cause temporary discomfort and minor bleeding but demonstrates high success rates for grade 2-3 internal hemorrhoids.
Sclerotherapy uses chemical solution injections into hemorrhoid veins to destroy tissue and shrink enlarged vessels. This procedure causes minimal pain and may be less effective than banding but works well for smaller internal hemorrhoids.
Coagulation Techniques including infrared photocoagulation, electrocoagulation, and bipolar coagulation use heat or electrical current to block blood supply and shrink small, bleeding internal hemorrhoids. These procedures produce few side effects and minimal discomfort.
External Hemorrhoid Thrombectomy involves surgical removal of blood clots from external hemorrhoids under local anesthesia for prompt pain relief. Best results occur when performed within 72 hours of symptom onset.
Hemorrhoid Artery Embolization (HAE) represents a minimally invasive, non-surgical treatment specifically designed for internal hemorrhoids. This procedure targets blood flow causing hemorrhoid formation, reducing inflammation and swelling while providing effective, long-term relief.
HAE Benefits and Success Rates
| Feature | HAE | Traditional Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Success Rate | 97% clinical success | 95% success |
| Recovery Time | Few days | 2-4 weeks |
| Pain Level | Minimal | Moderate to severe |
| Tissue Removal | None | Yes |
| Infection Risk | Very low | Higher |
| Bleeding Risk | Minimal | Moderate |
HAE offers significant advantages over traditional surgery including no tissue cutting or removal, minimal pain, reduced bleeding and infection risks, shorter recovery periods, and outpatient procedure convenience.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery becomes necessary for large, severe, or prolapsed hemorrhoids when other treatments fail to provide adequate relief or when complications develop.
Hemorrhoidectomy involves complete removal of external or prolapsed internal hemorrhoids and surrounding tissue through surgical incision. This procedure requires local or general anesthesia and demonstrates high success rates for severe cases.
Hemorrhoid Stapling (Hemorrhoidopexy) removes or repositions prolapsed internal hemorrhoidal tissue back inside the anus using surgical staples. This procedure requires anesthesia but typically produces less post-operative pain than traditional hemorrhoidectomy.
Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization (THD) uses sutures to tie off internal hemorrhoids and pull them back into normal position. This technique preserves tissue while addressing blood supply issues.
Treatment choice depends on hemorrhoid type, severity, patient preferences, and surgeon recommendations. Surgery represents the most invasive option, typically reserved when other interventions prove unsuccessful.
5 common questions people often ask about “how long do hemorrhoids last”
1. How long do hemorrhoids usually last?
The duration of hemorrhoids varies widely depending on their type and severity. Small external hemorrhoids may clear up on their own within a few days without treatment. Larger external hemorrhoids can take several weeks to heal and may cause significant discomfort. Internal hemorrhoids often last longer and sometimes require medical treatment. Mild cases typically resolve in a few days to a couple of weeks, while severe or thrombosed hemorrhoids can persist for several weeks or more.
2. What factors affect how long hemorrhoids last?
Several factors influence the duration of hemorrhoids, including the size and type (internal or external), severity of symptoms, presence of complications like thrombosis, and underlying causes such as constipation, straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, or sedentary lifestyle. Lifestyle habits like diet low in fiber, prolonged sitting, and chronic diarrhea or constipation can prolong healing or cause recurrence.
3. Can hemorrhoids go away on their own without treatment?
Yes, many hemorrhoids, especially small external ones, can resolve without medical intervention within a few days to weeks if aggravating factors are avoided. Home remedies such as sitz baths, increased fiber intake, hydration, and over-the-counter creams can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. However, persistent or severe hemorrhoids often require professional treatment to fully resolve.
4. When should I see a doctor about hemorrhoids?
You should consult a healthcare professional if hemorrhoid symptoms do not improve within a few days, if there is significant pain, bleeding, prolapse (hemorrhoids protruding outside the anus), or if symptoms worsen. Long-lasting hemorrhoids can lead to complications such as thrombosis or infection, so medical evaluation is important for persistent or severe cases.
5. Can hemorrhoids come back after treatment, and how can I prevent recurrence?
Yes, hemorrhoids can recur after treatment, especially if risk factors are not addressed. Preventive measures include eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding straining during bowel movements, not sitting for prolonged periods, and maintaining regular physical activity. Managing constipation and diarrhea promptly also helps reduce the risk of new hemorrhoids forming.
References
1. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS) Clinical Practice Guidelines
This is a primary reference for specialists, summarizing evidence from numerous studies.
Title: The 2018 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hemorrhoids
Authors: Davis, B. R., Lee-Kong, S. A., Migaly, J., Feingold, D. L., & Steele, S. R.
Source: Diseases of the Colon & Rectum
Key Findings:
“Hemorrhoids are common, with many patients having resolution of symptoms with dietary modification alone.”
For grade I and II internal hemorrhoids, conservative measures (fiber, stool softeners, topical agents) are usually sufficient. The response time is typically within days to a few weeks.
For an acute thrombosed external hemorrhoid (<72 hours), an excision can provide rapid pain relief. Otherwise, the pain will naturally subside over several days, but the lump may take weeks to fully resolve.
2. Clinical Review in the World Journal of Gastroenterology
This article provides a comprehensive overview of hemorrhoid pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management.
Title: Hemorrhoids: From basic pathophysiology to clinical management
Author: Varut Lohsiriwat
Source: World Journal of Gastroenterology
Key Findings:
“Acute symptoms of hemorrhoids usually last for a few days.”
Regarding thrombosed external hemorrhoids: “The pain is most severe within the first 48 h and spontaneously subsides over the next 4-5 d. The thrombosed mass may take several weeks to resolve completely.”
Link: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i17/2009.htm
3. Information from Harvard Medical School
A trusted source of evidence-based health information for the public.
Title: Hemorrhoids and what to do about them
Author: Harvard Health Publishing (Harvard Medical School)
Source: Harvard Health Blog
Key Findings:
“With simple measures, the pain and swelling of most symptomatic hemorrhoids should start to subside in two to three days. Overall improvement may take a week or two.”
For thrombosed hemorrhoids: “The pain of a thrombosed hemorrhoid should improve within 7 to 10 days without surgery. The hemorrhoid itself should shrink over the next few weeks.”
Link: https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/hemorrhoids_and_what_to_do_about_them
4. Information from Mayo Clinic
A leading global hospital and research center that provides patient-friendly medical information.
Title: Hemorrhoids
Author: Mayo Clinic Staff
Source: Mayo Clinic
Key Findings:
“Often, hemorrhoid symptoms go away within a week. See your healthcare provider if you don’t get relief in a week, or sooner if you have severe pain or bleeding.”
The clinic emphasizes that mild symptoms often respond well to home care remedies.
Link: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hemorrhoids/symptoms-causes/syc-20360268
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.