“How Often Should You Masturbate?” Discover how often you should masturbate for optimal health. Learn what science, doctors, and real users say about safe solo sex frequency.

Is masterbate good for your health?
Masturbation frequency remains one of the most misunderstood aspects of human sexuality, with no universal “correct” answer that applies to everyone. This natural sexual behavior varies dramatically among individuals based on age, gender, hormonal fluctuations, relationship status, and personal preferences. Research from the Kinsey Institute reveals that masturbation patterns differ significantly across demographics, while Pornhub Insights data shows contemporary trends in solo sexual activity continue evolving with digital technology.
This comprehensive guide examines scientific evidence surrounding optimal masturbation frequency, explores health benefits and potential risks, addresses cultural perspectives, and provides practical guidance for maintaining healthy sexual habits. We’ll analyze average frequencies by demographic groups, discuss when self-pleasure becomes problematic, examine relationship dynamics, and offer strategies for achieving personal balance in your sexual wellness routine.
Average Masturbation Frequency by Age and Gender
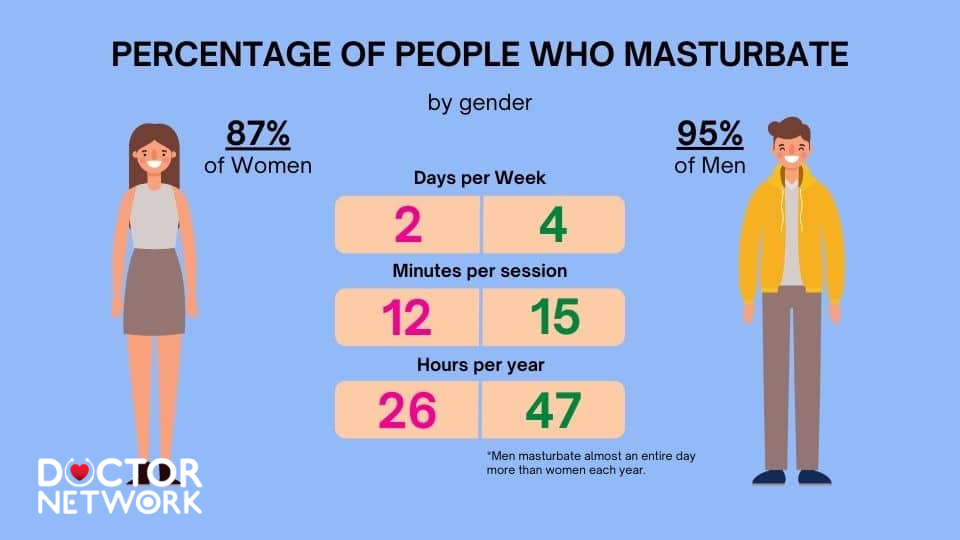
Percentage of People Who Masterbate by gender
Scientific Data on Masturbation Patterns
Men typically masturbate 2-5 times per week according to research published by Hims and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This frequency represents the median range observed across multiple demographic studies, though individual variation remains substantial. Testosterone levels, stress factors, and lifestyle circumstances significantly influence these patterns.
Women engage in solo sexual activity approximately 1-3 times weekly based on data from Healthline and MindBodyGreen publications. Female masturbation frequency correlates closely with menstrual cycles, estrogen fluctuations, and relationship satisfaction levels. Research indicates women’s self-pleasure habits often increase during ovulation periods when libido naturally peaks.
Age-related decline affects both genders as hormonal production decreases and life responsibilities expand. Young adults typically report higher frequencies compared to older demographics, with notable drops occurring after age 40 for men and during perimenopause for women.
| Age Group | Male Frequency (per week) | Female Frequency (per week) |
|---|---|---|
| 18-25 | 4-7 times | 2-4 times |
| 26-35 | 3-5 times | 2-3 times |
| 36-45 | 2-4 times | 1-3 times |
| 46-55 | 1-3 times | 1-2 times |
| 55+ | 1-2 times | 0-2 times |
Solo Sex Versus Sexual Dysfunction
Regular masturbation does not indicate sexual problems or addiction in most cases. Singles and partnered individuals both engage in self-stimulation for different reasons – singles for sexual release and partnered people for supplementing intimacy or addressing libido mismatches. Sexual behavior patterns reveal that coupled individuals often maintain consistent masturbation habits regardless of partner availability.
Distinguishing between healthy sexual expression and compulsive behavior requires examining motivation, frequency impact on daily functioning, and emotional responses following sexual activity. Orgasm frequency through masturbation often complements rather than replaces partnered sexual experiences.
Health Benefits of Masturbation in Moderation
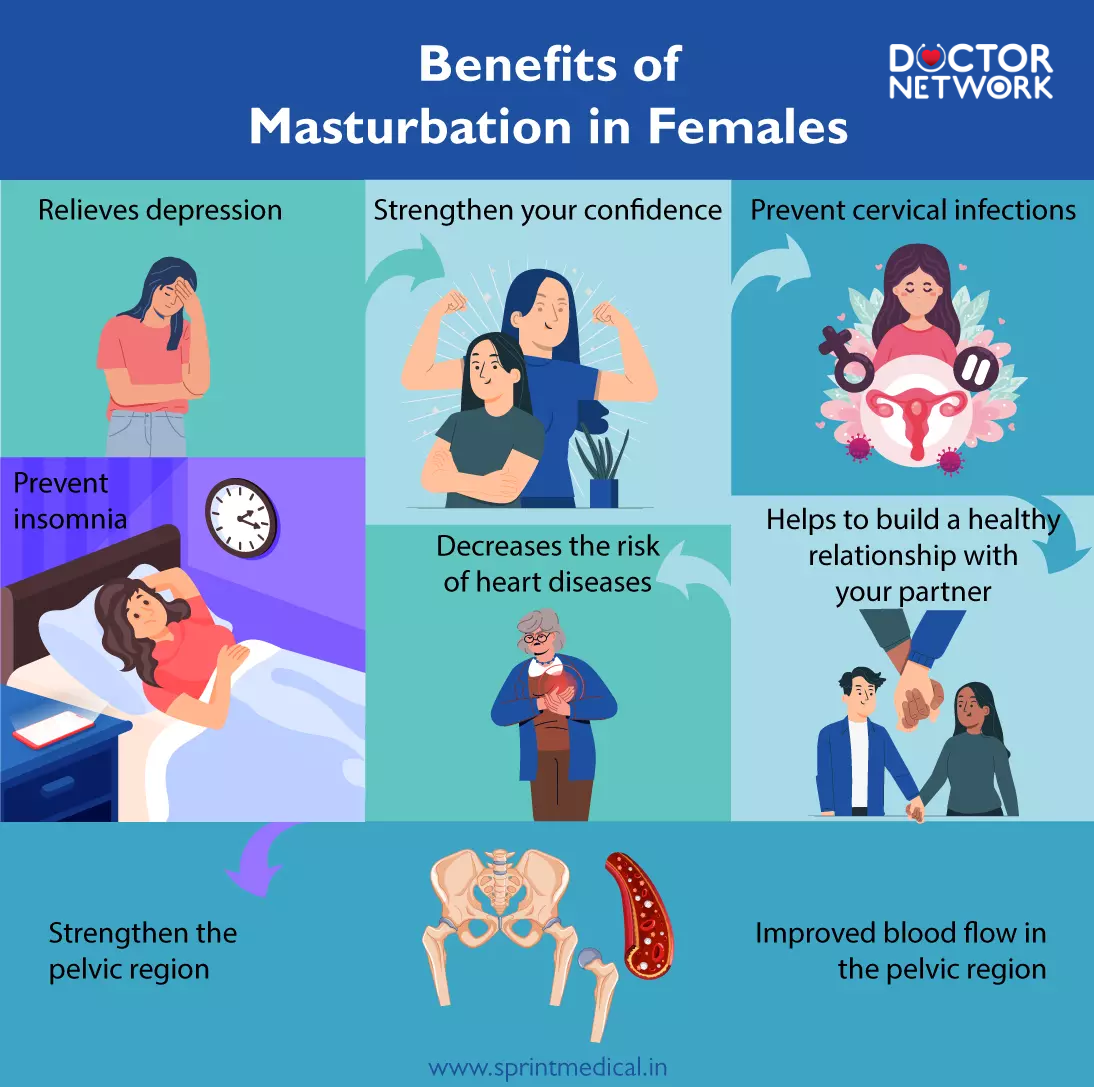
Benefits of Masturbation in Females
Prostate Cancer Risk Reduction
Harvard Health research demonstrates that men who ejaculate 21 or more times monthly reduce prostate cancer risk by approximately 33%. This protective effect stems from regular prostate stimulation and toxin elimination through ejaculatory fluid. The Harvard study followed 29,342 men over 18 years, providing robust evidence for this health benefit.
Prostate health improvement occurs through multiple mechanisms during masturbation. Regular ejaculation helps flush potentially harmful substances from prostate tissue while maintaining healthy blood flow to reproductive organs. Urologists increasingly recommend consistent sexual activity, including masturbation, as part of comprehensive prostate wellness strategies.
Neurochemical Benefits for Sleep and Mental Health
Dopamine, oxytocin, and prolactin release during orgasm creates powerful relaxation responses that improve sleep quality and emotional regulation. These neurotransmitters work synergistically to reduce cortisol levels, alleviate anxiety symptoms, and promote restful sleep patterns. Mental well-being improvements often occur within hours of sexual activity.
Hormone regulation through masturbation helps stabilize mood fluctuations and reduces stress-related disorders. The dopamine release associated with orgasm activates reward pathways similar to other pleasurable activities, contributing to overall psychological balance when practiced mindfully.
Immune System Enhancement
Recent studies suggest masturbation may boost immunoglobulin A (IgA) levels, strengthening immune responses against common infections. Sexual arousal and orgasm trigger complex physiological cascades that enhance white blood cell activity and antibody production. These immune benefits appear most pronounced with moderate frequency rather than excessive activity.
Researchers from Wilkes University found individuals with 1-2 sexual encounters weekly showed higher IgA levels compared to those with no sexual activity or excessive frequency. This U-shaped curve suggests optimal immune benefits occur within specific frequency ranges.
When Masturbation Becomes Problematic
Identifying Compulsive Sexual Behavior
Compulsive masturbation manifests through uncontrollable urges that disrupt normal daily functioning. Warning signs include inability to reduce frequency despite negative consequences, persistent shame following sexual activity, and neglecting responsibilities to engage in masturbation. These patterns indicate potential behavioral addiction requiring professional intervention.
Shame cycles often accompany problematic masturbation, creating emotional distress that paradoxically increases compulsive behaviors. Individuals may experience temporary relief through sexual activity followed by intense guilt, perpetuating destructive patterns that interfere with work, relationships, and self-esteem.
Neurochemical Imbalances and Mental Health
Excessive masturbation can disrupt dopamine regulation, leading to tolerance effects similar to other addictive behaviors. The cue-action-reward-regret cycle creates neurological patterns that require increasingly intense stimulation for satisfaction. Dopamine fatigue may result in emotional numbing, depression, and anxiety symptoms.
Behavioral addiction research reveals that compulsive sexual activities activate brain regions identical to substance dependencies. The anterior cingulate cortex and nucleus accumbens show hyperactivity during sexual urges, while prefrontal control areas demonstrate decreased functioning.
Clinical Classifications and Diagnostic Criteria
The World Health Organization’s ICD-11 recognizes Compulsive Sexual Behavior Disorder (CSBD) as a legitimate mental health condition. However, the DSM-5 does not currently classify sex addiction as a distinct disorder, creating ongoing debate within psychiatric communities. WHO guidelines emphasize functional impairment rather than frequency alone as diagnostic criteria.
Key diagnostic indicators include:
- Repetitive sexual behaviors becoming central life focus
- Unsuccessful attempts to reduce sexual activity
- Continued behavior despite negative consequences
- Significant distress or impairment in functioning
Missing Perspectives That Matter
Masturbation and Body Image Relationships
Individuals with poor body image often use masturbation as emotional compensation for low self-esteem and sexual insecurity. Solo sexual activity may provide temporary validation while avoiding perceived judgment from partners. Sexual self-esteem correlates strongly with masturbation frequency and satisfaction levels.
Body dysmorphia and appearance anxiety can drive compulsive masturbation patterns as individuals seek comfort through sexual pleasure. Therapeutic interventions addressing underlying self-image issues often prove more effective than frequency restriction alone for problematic behaviors.
LGBTQ+ Sexual Identity Exploration
Sexual minorities frequently utilize masturbation for identity exploration and self-discovery during coming-out processes. Solo sexual experiences provide safe environments for understanding personal preferences without external pressure or judgment. This exploration proves particularly valuable for individuals questioning their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Masturbation serves crucial roles in LGBTQ+ sexual development, allowing experimentation with different fantasies, techniques, and sensations. Community resources and sex-positive education help normalize these experiences within sexual minority populations.
Technology-Enhanced Sexual Experiences
Virtual reality pornography, AI-powered sex robots, and interactive adult content increasingly influence modern masturbation practices. Companies like Oculus, Replika, and RealDoll create immersive sexual experiences that may affect real-world intimacy expectations. These technologies raise concerns about attachment to artificial stimulation over human connection.
Digital intimacy through technology-enhanced masturbation potentially creates unrealistic expectations for partnered sex. Overstimulation through high-intensity virtual experiences may contribute to decreased satisfaction with conventional sexual activities and partners.
Cultural, Religious, and Moral Perspectives
Eastern Versus Western Cultural Attitudes
Eastern cultures traditionally view masturbation through restrictive lenses influenced by Buddhist and Confucian teachings emphasizing self-discipline and energy conservation. Shame and secrecy surround solo sexual activities in many Asian societies, despite changing attitudes among younger generations. Traditional Chinese medicine considers excessive masturbation depleting to vital energy (qi).
Western perspectives increasingly frame masturbation as healthy self-care and sexual empowerment, particularly following feminist and sex-positive movements. European and North American sex education emphasizes masturbation benefits while encouraging open discussions about sexual wellness and pleasure.
Religious Doctrines on Self-Pleasure
Catholic doctrine traditionally condemns masturbation as sinful, viewing sexual pleasure outside procreative purposes as morally problematic. Pope Francis and contemporary Catholic theologians maintain these positions while acknowledging pastoral sensitivity in addressing sexual struggles. Thomas Aquinas’s theological framework continues influencing Catholic sexual ethics.
Islamic perspectives on masturbation vary significantly among scholars and denominations. While some interpret Quranic teachings as prohibiting self-pleasure, others permit masturbation as preferable to extramarital sexual activity. Contemporary Islamic scholars increasingly recognize masturbation’s role in preventing sexual sin.
Buddhist philosophy emphasizes desire restraint and mindful awareness regarding sexual urges. The Dalai Lama and other Buddhist leaders teach moderation rather than complete abstinence, encouraging practitioners to examine motivations behind sexual behaviors.
| Religion | Official Position | Modern Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Catholicism | Generally prohibited | Increasing pastoral understanding |
| Islam | Varies by school | Context-dependent acceptance |
| Buddhism | Moderation emphasized | Mindful practice encouraged |
| Judaism | Traditionally discouraged | Reform movements more accepting |
| Protestantism | Varies by denomination | Often viewed as natural |
Philosophical Frameworks: Freedom Versus Self-Control
Stoic philosophy, exemplified by Marcus Aurelius’s teachings, emphasizes mastering desires as pathways to inner peace and personal freedom. The central question becomes whether individuals control their urges or submit to compulsive patterns that diminish autonomy and self-determination.
Contemporary philosophical debates examine masturbation through autonomy, consent, and personal empowerment lenses. Sex-positive feminism argues that claiming sexual pleasure represents liberation from societal constraints, while critics worry about commodification of sexuality through pornography consumption.
Masturbation and Romantic Relationships
Solo Sexual Activity Within Committed Partnerships
Partnered individuals frequently continue masturbating to fulfill unmet sexual needs, explore personal fantasies, or address libido mismatches with their significant others. Research indicates that 85% of men and 78% of women in relationships maintain regular masturbation habits regardless of sexual satisfaction levels with partners.
The distinction between fulfilling legitimate sexual needs versus emotional betrayal creates relationship tension for many couples. Communication patterns, sexual compatibility, and individual autonomy expectations significantly influence how partners perceive solo sexual activities within committed relationships.
Impact on Intimate Relationships and Sexual Performance
Excessive pornography consumption during masturbation may contribute to desensitization and unrealistic expectations for partnered sex. Porn-induced erectile dysfunction (PIED) affects increasing numbers of young men who struggle with arousal during real-world sexual encounters after frequent high-stimulation masturbation habits.
Sexual compatibility issues arise when masturbation preferences conflict with partner capabilities or comfort levels. Individuals accustomed to specific stimulation patterns through solo sex may experience difficulty achieving satisfaction through conventional partnered activities.
Communication Strategies for Couples
Dr. Emily Nagoski and Esther Perel emphasize open dialogue about masturbation as essential for healthy relationship dynamics. Couples who discuss solo sexual activities report higher satisfaction levels and reduced anxiety about partner fidelity or sexual adequacy.
Effective communication approaches include:
- Discussing individual sexual needs without judgment
- Establishing boundaries around pornography use
- Exploring how masturbation can complement partnered sex
- Addressing insecurities about sexual performance or attractiveness
- Creating agreements about frequency and privacy expectations
How to Balance and Optimize Your Masturbation Habits
Finding Your Personal “Sweet Spot”
The frequently cited range of 7-21 masturbation sessions monthly represents a general guideline rather than rigid prescription for optimal frequency. Individual factors including age, health status, relationship circumstances, and personal preferences determine appropriate ranges for each person. Post-masturbation emotional responses provide valuable feedback for assessing whether current habits support overall well-being.
Relief, relaxation, and satisfaction following masturbation indicate healthy patterns that contribute positively to sexual wellness. Conversely, guilt, shame, or compulsive urges suggest potential imbalances requiring attention and possible modification of frequency or technique.
Mindful Masturbation Practices
Combining masturbation with breathwork, meditation, and intentional awareness transforms routine sexual activity into meaningful self-care practice. Mindful approaches emphasize bodily sensations, emotional responses, and present-moment awareness rather than goal-oriented performance or fantasy escape.
Pornography-free masturbation encourages deeper connection with personal sexuality and reduces dependency on external stimulation. This approach helps individuals develop greater awareness of natural arousal patterns and personal preferences independent of artificial enhancement.
Self-Monitoring Tools and Digital Wellness
Applications like Streaks, NoFap counters, and Notion templates enable systematic tracking of masturbation frequency and associated mood patterns. Digital wellness approaches treat sexual activity similarly to nutrition, exercise, or sleep hygiene – as manageable aspects of overall health requiring awareness and intentional regulation.
Effective self-monitoring strategies include:
- Recording frequency, duration, and emotional states
- Identifying triggers and patterns in masturbation habits
- Setting realistic goals for frequency modification
- Tracking correlations with stress, sleep, and relationship factors
- Celebrating progress without perfectionist expectations
Self-tracking tools from the NoFap community provide peer support and accountability for individuals seeking to modify masturbation habits. However, balanced approaches avoid extreme abstinence goals that may create additional stress or shame around natural sexual behaviors.
Finding Your Personal Balance
Optimal masturbation frequency varies dramatically among individuals based on biological, psychological, and social factors unique to each person’s circumstances. Rather than pursuing arbitrary numerical targets, focus on cultivating awareness of how sexual habits impact overall well-being, relationships, and daily functioning.
Masturbation itself is neither inherently beneficial nor harmful – the relationship you develop with this natural behavior reflects broader patterns of self-care, emotional regulation, and sexual wellness. Healthy approaches emphasize mindful awareness, open communication with partners when applicable, and professional support when patterns become problematic or distressing.
The journey toward sexual wellness requires honest self-assessment, cultural awareness, and willingness to adapt habits as life circumstances evolve. By understanding scientific evidence, cultural perspectives, and personal needs, individuals can develop sustainable approaches to masturbation that support rather than hinder their overall health and happiness.
Frequently asked questions about the topic “How often should you masturbate?”
1. How often is it healthy to masturbate?
There is no specific “right” frequency for masturbation that applies to everyone. Masturbation is a normal and healthy activity, and the frequency varies widely among individuals. As long as it does not interfere with your daily life, responsibilities, or relationships, masturbating as often as you feel comfortable is generally considered healthy.
2. Can masturbating too often be harmful?
Masturbating excessively to the point where it causes physical irritation, pain, or interferes with daily activities, work, or social life may be problematic. However, for most people, masturbation is a safe activity. If you feel it is becoming compulsive or affecting your mental health, it might be helpful to talk to a healthcare professional.
3. Does masturbating affect sexual performance or health?
Masturbation does not negatively affect sexual performance or health. In fact, it can help people learn about their bodies, improve sexual satisfaction, and reduce stress. It is a natural way to explore sexual feelings and can complement a healthy sex life.
4. Is it normal to masturbate daily?
Yes, it is normal for some people to masturbate daily. Frequency varies from person to person, and daily masturbation is not harmful if it feels good and does not disrupt your life. Everyone’s sexual needs and desires are different, so what is normal for one person may differ for another.
5. Can masturbation replace sex with a partner?
Masturbation and partnered sex serve different purposes and experiences. Masturbation can be a healthy part of sexual expression, but it does not replace the emotional intimacy and connection that often come with sex with a partner. Both can coexist and contribute to a fulfilling sexual life.
References
Harvard Prostate Cancer Study: https://www.europeanurology.com/article/S0302-2838(16)00377-8/fulltext
National Survey of Sexual Health and Behavior – Masturbation Prevalence: https://jsm.jsexmed.org/article/S1743-6095(15)32943-9/fulltext
World Health Organization – Compulsive Sexual Behaviour Disorder: https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/frequently-asked-questions/compulsive-sexual-behaviour-disorder
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.