Nutritional excess and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to the emergence of obesity at all ages, with a rising trend among the elderly. Obesity in the elderly can be the root cause of various diseases such as cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal disorders, and diabetes, significantly impacting the quality of life and lifespan. An obese elderly individual may experience a reduction of up to 20% in their life expectancy. Let’s explore this issue through the following article by Assoc. Prof. Nguyen Anh Tuan, MD, Ph.D.
1. Causes of Obesity in the Elderly
As age advances, the metabolic rate in the body decreases, resulting in reduced energy intake for the elderly compared to when they were younger. This promotes the risk of obesity in the elderly.
With increasing age, muscle mass decreases, leading to a reduced energy requirement to sustain bodily functions. Providing excess energy in this scenario leads to overweight and obesity in the elderly.
Digestive absorption efficiency decreases, causing deficiencies in certain essential substances such as vitamin B12 (critical for converting fat into energy), making the elderly more susceptible to obesity.

Elderly individuals tend to be more susceptible to obesity in comparison to younger age groups
The dietary habits of the elderly are often high in protein and rich in nutrients but lack physical activity, involving the use of nutritional products, supplements, and medications to extend lifespan, such as royal jelly, sheep placenta, which can contribute to obesity.
Physical activity tends to decrease after retirement. Both physical and mental activities decline, leading to less brain and muscle energy consumption.
2. Serious Consequences of Obesity in the Elderly
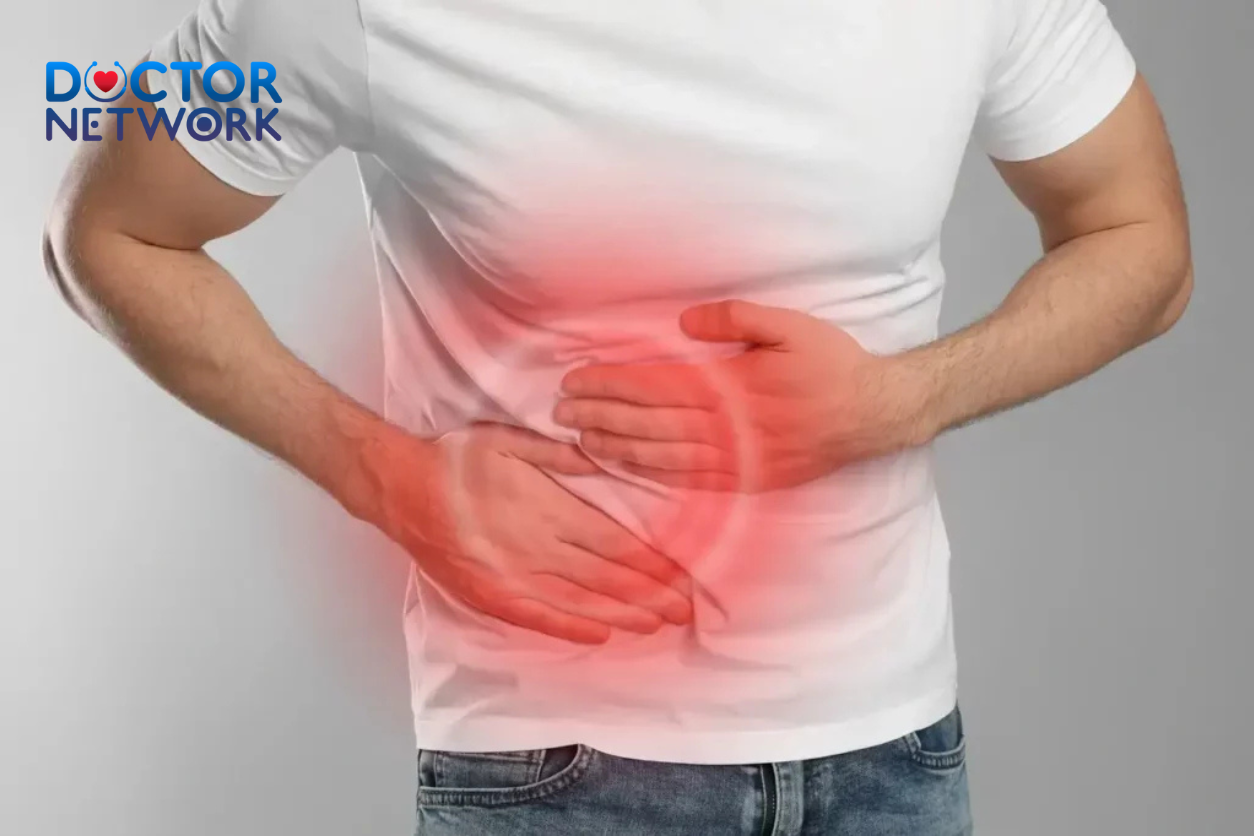
Obesity disrupts body balance, making it cumbersome and slow. The consequences of overweight and obesity include a reduction in both physical and life quality. Obesity in the elderly often gives rise to the following health issues:
- Musculoskeletal disorders: joint degeneration, osteoporosis, gout – joint pain due to the pressure exerted by body weight. Knee joints and the spine are the earliest affected.
- Cardiovascular diseases: dyslipidemia causing arterial plaque formation, hypertension, stroke, and heart failure. Currently, cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death in the elderly, with many cases being complications of obesity.
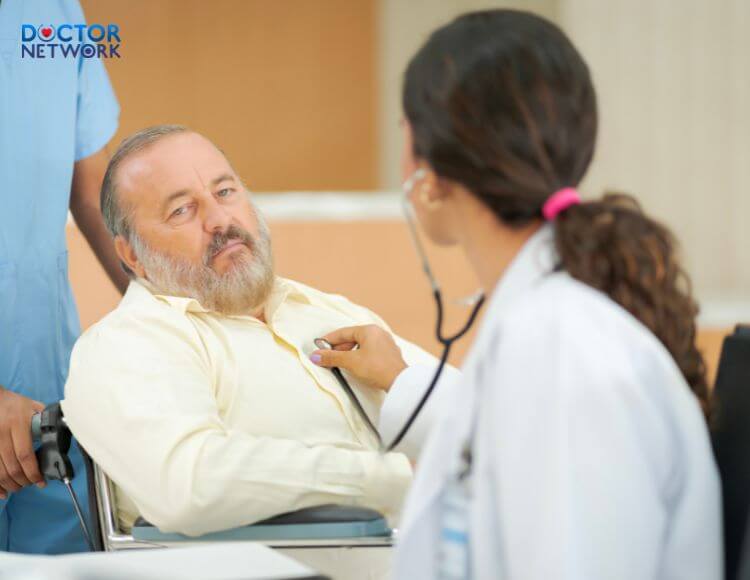

Heart disease can be a complication of obesity
- Diabetes: Obesity is closely associated with type 2 diabetes due to insulin resistance.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: constipation, hemorrhoids, colorectal cancer, fatty liver disease, which, if not timely treated, can lead to liver fibrosis and metabolic fat stone formation.
- Obesity contributes to memory decline and increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in the elderly.
- Respiratory diseases: restricted lung and bronchial activities in obese individuals often lead to breathing rhythm disorders, snoring, and sleep apnea. The severity of breathing rhythm disorders increases with the degree of obesity.
- Sexual dysfunction: decreased endocrine function, reduced health, and the heavy body make obese individuals more prone to sexual dysfunction, encountering difficulties in marital relationships.
- Obesity and cancer risk: Some studies show a correlation between obesity and cancers such as esophageal, colorectal, breast, cervical, liver, and prostate cancers.
- Obesity reduces lifespan: Recent scientific studies have proven that obesity can decrease lifespan by 6-8 years.
3. Treatment of Obesity in the Elderly
3.1. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting an active lifestyle and cultivating positive rest habits. For the elderly with varying degrees of functional decline, physical activity can be as simple as changing postures during daily activities or slow, gentle movements with a cane or walker. Eliminate unhealthy snacking habits.
3.2. Dietary Habits Modification
Consume more green vegetables and fruits, limit sugar intake…
3.3. Exercise
For the elderly, cardiovascular and musculoskeletal diseases are common, so before exercising, a comprehensive health check is necessary. Consultation with doctors and exercise specialists about physical activities is essential to determine the most suitable exercise for each elderly person with obesity.

Physical exercise helps improve obesity-related health conditions
3.4. Establish Weight Monitoring Habits
The elderly should regularly monitor their BMI to detect sudden weight gain or loss, which requires examination to determine the cause.
Elderly individuals experience metabolic decline and reduced physical activity but are often provided with excessive nutrition, leading to overweight and obesity. Complications such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and musculoskeletal disorders are highly likely to occur. Establishing a healthy lifestyle, adopting a balanced diet, and regularly monitoring weight are crucial factors in reducing overweight and obesity in the elderly.
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.