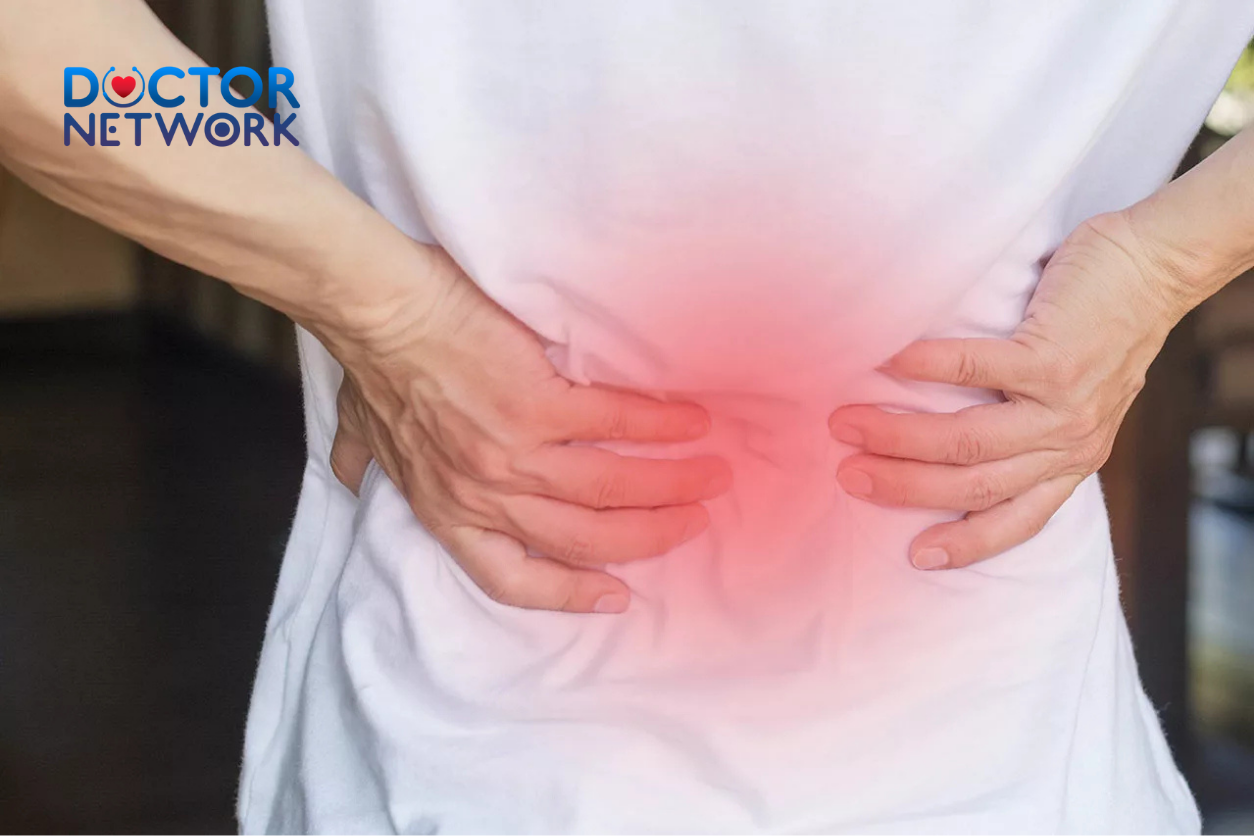
Sharp pain in the right back can be a distressing and debilitating experience, often signaling underlying health issues that require attention. This discomfort, which can range from a sudden, stabbing sensation to a persistent ache, may originate from various structures within the back, including muscles, nerves, bones, or even internal organs. Understanding the root cause of this pain is crucial for effective treatment and long-term relief. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the common causes of sharp right back pain, discuss symptoms and diagnostic approaches, outline treatment options, and provide strategies for prevention.
Understanding the Anatomy of Right Back Pain
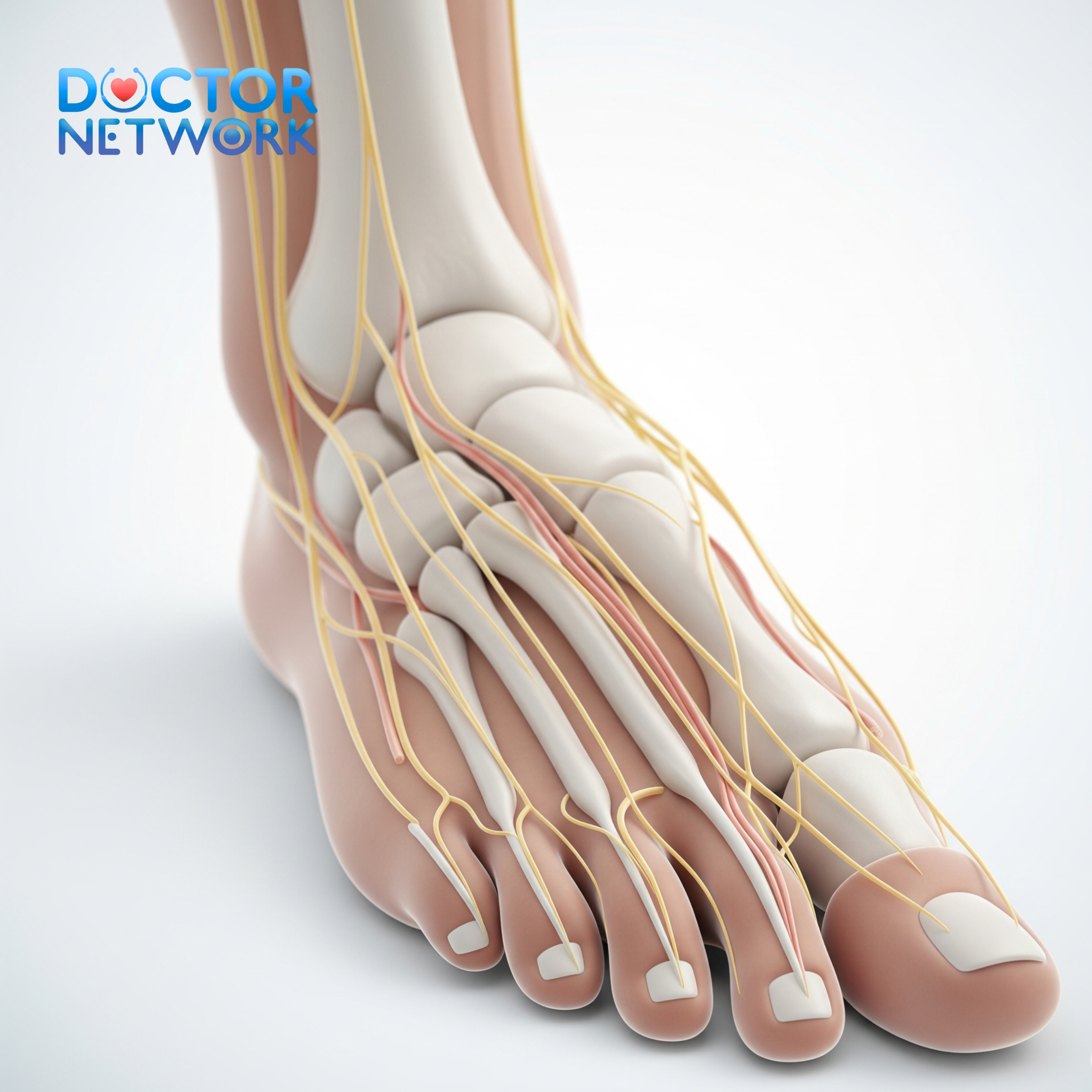
The right back region encompasses a complex network of anatomical structures, each of which can potentially contribute to pain:
- Muscles: Including the trapezius, latissimus dorsi, and erector spinae
- Bones: Ribs, vertebrae, and associated joints
- Nerves: Spinal nerves and peripheral nerve roots
- Organs: Kidneys, liver, and gallbladder

The right back region encompasses a complex network of anatomical structures
When sharp pain occurs in this area, it’s essential to consider both musculoskeletal and internal organ-related causes.
Common Causes of Sharp Right Back Pain
1. Muscular Strain and Spasm
Muscle-related pain is one of the most frequent culprits behind sharp right back discomfort.
| Cause | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Overexertion | Sudden, intense pain; muscle tightness | Rest, ice/heat therapy, gentle stretching |
| Poor posture | Dull ache that becomes sharp with movement | Posture correction, ergonomic adjustments |
| Trauma | Acute pain, possible bruising | Medical evaluation, pain management |
2. Spinal Disc Issues
Problems with the intervertebral discs can lead to sharp, radiating pain in the right back.
- Herniated disc: When the soft inner core of a disc protrudes through the tougher exterior

When the soft inner core of a disc protrudes through the tougher exterior
- Bulging disc: A disc that extends beyond its normal boundary but hasn’t ruptured
- Degenerative disc disease: Age-related wear and tear on spinal discs
Symptoms often include sharp pain that may radiate to the buttocks or legs, accompanied by numbness or tingling sensations.
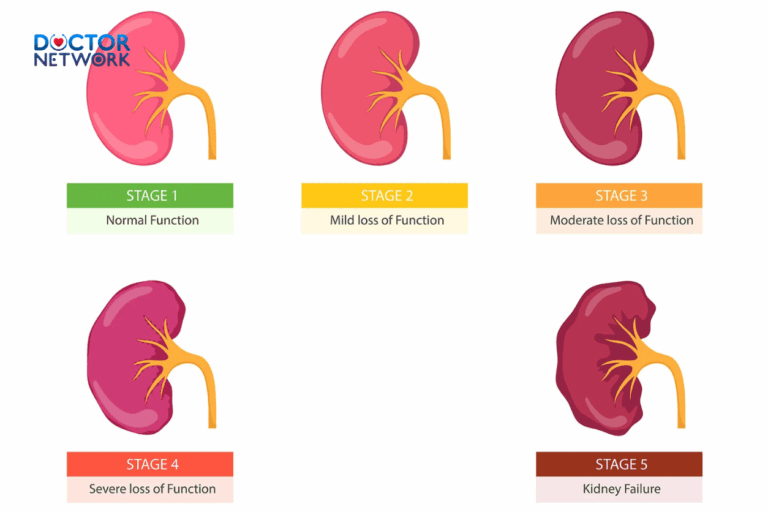
3. Kidney Problems
Kidney-related issues can manifest as sharp pain in the right back, often accompanied by other symptoms:
- Kidney stones
- Pyelonephritis (kidney infection)
- Renal cysts
Key differentiator: Kidney pain is typically felt in the flank area, just below the ribcage, and may be associated with urinary symptoms or fever.
4. Facet Joint Arthritis
Inflammation of the small joints in the spine can cause localized sharp pain, especially during movement or when pressure is applied to the affected area.
5. Rib-Related Pain
Conditions affecting the ribs, such as fractures, costochondritis (inflammation of rib cartilage), or intercostal muscle strain, can produce sharp pain in the right back.
Identifying Symptoms and Seeking Help
When experiencing sharp right back pain, pay attention to these key factors:
- Pain characteristics:
- Intensity (mild, moderate, severe)
- Duration (acute vs. chronic)
- Quality (stabbing, burning, aching)
- Associated symptoms:
- Neurological signs (numbness, weakness)
- Systemic symptoms (fever, unexplained weight loss)
- Aggravating and alleviating factors
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe, unrelenting pain
- Pain accompanied by fever, chills, or night sweats
- Neurological symptoms (loss of bladder/bowel control, leg weakness)
- Pain following trauma or a fall
For persistent pain lasting more than a few weeks or pain that interferes with daily activities, consult your healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation.
Treatment Options for Sharp Right Back Pain
Treatment approaches vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the pain:
Conservative Management
- Pain relief medications:
- Over-the-counter NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen, naproxen)
- Acetaminophen for pain without inflammation
- Prescription medications for severe cases
- Physical therapy:
- Targeted exercises to strengthen core and back muscles
- Manual therapy techniques
- Posture correction and body mechanics training
- Hot and cold therapy:
- Ice for acute injuries (first 48-72 hours)
- Heat for chronic pain and muscle relaxation
- Alternative therapies:
- Acupuncture
- Chiropractic care
- Massage therapy
Advanced Interventions
For cases that don’t respond to conservative treatment:
- Epidural steroid injections: To reduce inflammation around nerve roots
- Radiofrequency ablation: For chronic facet joint pain
- Surgery: Reserved for severe cases or when conservative measures fail
Preventing Sharp Right Back Pain
Proactive measures can significantly reduce the risk of experiencing sharp right back pain:
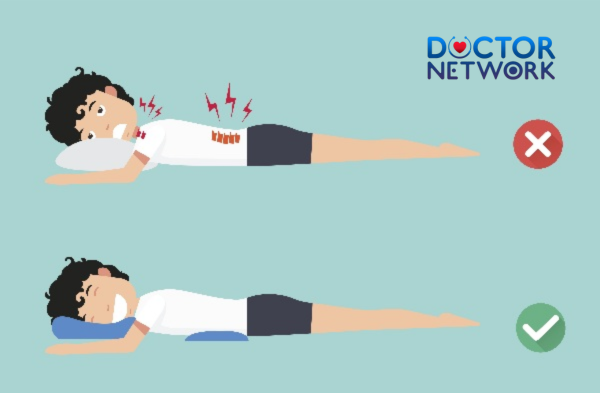
- Maintain proper posture:
- Use ergonomic furniture and equipment
- Practice good posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping
- Exercise regularly:
- Focus on core-strengthening exercises
- Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming or yoga
- Practice safe lifting techniques:
- Bend at the knees, not the waist
- Keep the object close to your body
- Avoid twisting while lifting
- Manage stress:
- Engage in relaxation techniques (e.g., meditation, deep breathing)
- Seek professional help if stress is overwhelming
- Maintain a healthy weight:
- Excess weight puts additional strain on the back

Excess weight puts additional strain on the back
Frequently asked questions about “sharp pain in the right back”
1. Can sharp pain in the right back be a sign of liver problems?
While the liver is located in the upper right abdomen, liver problems can sometimes manifest as referred pain in the right back. However, this is less common than musculoskeletal causes. Liver-related pain is typically dull and constant rather than sharp. If you suspect liver issues, look for other symptoms such as:
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin or eyes)
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
Consult a hepatologist or gastroenterologist if you’re concerned about liver health.
2. How can I differentiate between kidney pain and muscle pain in my right back?
Distinguishing between kidney pain and muscle pain can be challenging, but there are some key differences:
| Kidney Pain | Muscle Pain |
|---|---|
| Deep, constant ache | Sharp, may vary with movement |
| Located below the ribcage | Can occur anywhere in the back |
| Often accompanied by urinary symptoms | Usually worsens with specific movements |
| May cause nausea or fever | Rarely causes systemic symptoms |
If you suspect kidney issues, such as pyelonephritis or nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), seek medical attention, especially if you experience fever, chills, or changes in urination.
3. Can anxiety cause sharp pain in the right back?
Yes, anxiety can manifest as physical symptoms, including sharp back pain. The mechanism involves:
- Muscle tension: Anxiety often leads to prolonged muscle contraction, particularly in the back and shoulders.
- Heightened pain sensitivity: Anxiety can lower pain thresholds, making normal sensations feel more intense.
- Stress-related inflammation: Chronic stress can increase inflammation throughout the body.
If anxiety is contributing to your back pain, consider cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness techniques alongside physical treatments.
4. What exercises can help alleviate sharp pain in the right back?
Gentle exercises can often help relieve sharp back pain, but it’s crucial to consult a physical therapist or doctor before starting any regimen. Some beneficial exercises include:
- Cat-Cow Stretch: Improves spine flexibility and relieves tension.
- Bird Dog: Strengthens core and promotes spinal stability.
- Gentle Twists: Increases spinal mobility and relieves muscle tension.
- Wall Slides: Improves posture and strengthens upper back muscles.
- Pelvic Tilts: Engages core muscles and promotes lower back flexibility.
Remember to start slowly and stop if pain increases. Proper form is essential to prevent further injury.
5. When should I worry about sharp pain in my right back?
While most cases of sharp back pain are not serious, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention:
- Severe, unrelenting pain
- Pain accompanied by fever (possible sign of infection)
- Neurological symptoms (numbness, weakness, or tingling in legs)
- Loss of bladder or bowel control (may indicate cauda equina syndrome)
- Pain following significant trauma
- Unexplained weight loss alongside back pain
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek emergency medical care. Conditions like spinal cord compression or abdominal aortic aneurysm require prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Scientific researches on “sharp pain in the right back”
- “Epidemiology of low back pain in adults” by Hoy et al., published in Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology. This study provides an overview of the prevalence and risk factors for low back pain, including right-sided pain.
- “Diagnosis and treatment of low back pain” by Deyo and Weinstein, published in the New England Journal of Medicine. This article discusses the various causes of low back pain, including right-sided pain, and treatment options.
- “Prevalence of and screening for serious spinal pathology in patients presenting to primary care settings with acute low back pain” by Henschke et al., published in Arthritis & Rheumatism. This study examines the frequency of serious causes of low back pain that may apply to right-sided low back pain.
- “Mechanisms of low back pain: a guide for diagnosis and therapy” by Allegri et al., published in F1000Research. This article delves into the pathophysiological mechanisms of low back pain, including low back pain.
- “Diagnosis and treatment of acute low back pain” by Casazza, published in American Family Physician. This study provides clinical practice guidance for the evaluation and management of acute low back pain that may apply to right-sided low back pain.
By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and implementing preventive strategies, you can effectively manage and potentially avoid sharp right back pain. Remember, persistent or severe pain should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
References:
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325252
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22864-lower-right-back-pain
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.