Creatinine, a waste product of muscle metabolism, serves as a crucial indicator of kidney function. Elevated creatinine levels in the blood often signal underlying health issues, particularly kidney problems. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of creatinine, its impact on health, and effective strategies to lower its levels naturally and medically. We’ll explore the causes of high creatinine, recognize its symptoms, and “How to reduce creatinine in the blood” for optimal kidney health.
Understanding Creatinine
What is Creatinine?
Creatinine is a byproduct of creatine phosphate breakdown in muscles. This organic compound plays a vital role in energy production for muscle contractions. Normal creatinine levels typically range from 0.6 to 1.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) in men and 0.5 to 1.1 mg/dL in women.

Creatinine is a byproduct of muscle metabolism, which is excreted from the body in urine
Why High Creatinine Levels Are a Concern
Elevated creatinine levels often indicate impaired kidney function. The kidneys, responsible for filtering waste products from the blood, may struggle to eliminate creatinine efficiently when damaged or diseased. High creatinine can result from various conditions, including:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- Acute kidney injury (AKI)
- Dehydration
- Muscle disorders
- Certain medications
How is Creatinine Measured?
Healthcare providers use blood tests to measure creatinine levels. The most common tests include:
- Serum creatinine test
- Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR)
- Creatinine clearance test
These tests help assess kidney function and detect potential renal issues early.
Causes of High Creatinine
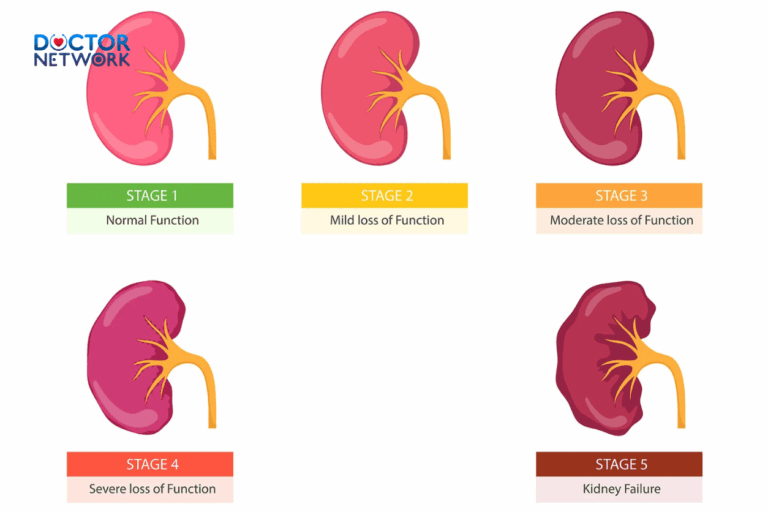
Kidney Disease
Kidney disease is the primary culprit behind elevated creatinine levels. Both acute and chronic kidney diseases can impair the organs’ ability to filter waste products effectively.
| Type of Kidney Disease | Characteristics | Impact on Creatinine |
|---|---|---|
| Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) | Progressive loss of kidney function | Gradual increase in creatinine |
| Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Sudden decrease in kidney function | Rapid rise in creatinine |
Muscle Breakdown
Excessive muscle breakdown, known as rhabdomyolysis, can lead to increased creatinine production. Causes include:
- Severe injuries
- Intense physical exertion
- Certain medications (e.g., statins)
- Genetic muscle disorders
Dehydration
Insufficient fluid intake or excessive fluid loss can concentrate creatinine in the blood, leading to elevated levels.
Medications
Some medications can affect creatinine levels or kidney function, including:
- Certain antibiotics (e.g., gentamicin)
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Chemotherapy drugs
Diet
A high-protein diet, particularly one rich in red meat, can increase creatinine production.
Recognizing the Symptoms of High Creatinine
Early Signs
Initial symptoms of elevated creatinine may include:
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea
- Swelling in extremities
Severe Symptoms
As creatinine levels continue to rise, more severe symptoms may manifest:
- Shortness of breath
- Muscle cramps
- Confusion
- Seizures
The Importance of Early Detection
Prompt identification of elevated creatinine levels is crucial for preventing further kidney damage and associated complications.
How to reduce creatinine in the blood
Diet Modifications
Dietary changes play a significant role in managing creatinine levels:
- Limit protein intake, especially from red meat
- Increase consumption of fiber-rich foods
- Incorporate kidney-friendly fruits and vegetables
Increase fiber-rich fruits and vegetables
Staying Hydrated
Proper hydration is essential for maintaining optimal kidney function and reducing creatinine levels. Aim for:
- 8-10 glasses of water daily
- Herbal teas and fresh fruit juices (in moderation)
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help manage creatinine levels:
- Low-impact exercises (e.g., walking, swimming)
- Yoga and stretching routines
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen

Exercise regularly, at least 30 minutes a day
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight can strain the kidneys. Maintain a healthy BMI through:
- Balanced diet
- Regular exercise
- Portion control
Medical Treatments for High Creatinine
Medications
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to address underlying causes of high creatinine:
- ACE inhibitors or ARBs for hypertension
- Phosphate binders for mineral imbalances
- Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for anemia
Dialysis
In severe cases of kidney dysfunction, dialysis may be necessary:
- Hemodialysis: Blood filtration through an external machine
- Peritoneal dialysis: Using the peritoneum as a natural filter
Kidney Transplant
For end-stage renal disease, a kidney transplant may be the most effective treatment option.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Creatinine Management
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
Long-term dietary recommendations include:
- Limiting sodium intake
- Avoiding processed foods
- Incorporating whole grains and lean proteins
Regular Exercise Routine
Develop a consistent exercise plan:
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly
- Include both cardiovascular and strength training exercises
Monitoring Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar
Regular monitoring of these vital signs is crucial for kidney health:
- Aim for blood pressure below 130/80 mm Hg
- Maintain blood glucose levels within the target range
Quitting Smoking
Smoking cessation can significantly improve kidney function and overall health.
Managing Stress
Implement stress-reduction techniques:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing exercises
- Regular sleep schedule
Disclaimer and Importance of Professional Advice
This information is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment of elevated creatinine levels. Always seek medical guidance before making significant changes to your diet, exercise routine, or medication regimen.
5 frequently asked questions related to “How to reduce creatinine in the blood”
What foods should I avoid to lower my creatinine levels?
To reduce creatinine levels in your blood, it’s advisable to limit or avoid:
- Red meat (beef, pork, lamb)
- Processed meats (sausages, bacon, deli meats)
- High-sodium foods (canned soups, pickles, salty snacks)
- Dairy products high in phosphorus (cheese, milk)
- Foods high in potassium if you have advanced kidney disease (bananas, oranges, potatoes)
Instead, focus on a renal-friendly diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins like fish or plant-based sources. Always consult with a registered dietitian or nephrologist for personalized dietary advice based on your specific kidney function and overall health status.
Can drinking more water help lower creatinine levels?
Yes, increasing your water intake can help lower creatinine levels in the blood. Proper hydration:
- Helps dilute the concentration of creatinine in the bloodstream
- Supports kidney function by promoting urine production and waste elimination
- Prevents dehydration, which can lead to elevated creatinine levels
Aim for 8-10 glasses (64-80 ounces) of water daily, unless your healthcare provider has advised fluid restrictions due to certain kidney conditions. Remember, other fluids like herbal teas and clear broths can contribute to your daily fluid intake as well.
How quickly can lifestyle changes reduce creatinine levels?
The timeline for reducing creatinine levels through lifestyle changes can vary depending on several factors:
- Severity of kidney dysfunction
- Underlying cause of elevated creatinine
- Consistency in implementing lifestyle changes
- Individual metabolic factors
Generally, you might start seeing improvements in 2-4 weeks with consistent dietary changes, increased hydration, and regular exercise. However, significant reductions may take several months. It’s crucial to:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations consistently
- Attend regular check-ups to monitor your progress
- Be patient, as sustainable improvements take time
Remember, lifestyle changes not only help reduce creatinine but also support overall kidney health and function in the long term.
Are there any supplements that can help lower creatinine levels?
While some supplements may support kidney function, it’s essential to approach them cautiously and always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen. Some supplements that have shown potential in supporting kidney health include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: May help reduce inflammation and support kidney function
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that may help protect kidney cells (but excessive amounts can be harmful)
- Coenzyme Q10: May support cellular energy production in the kidneys
- Astragalus: An herb traditionally used in Chinese medicine for kidney support
However, it’s crucial to note:
- Supplements are not regulated as strictly as medications
- Some supplements can interact with medications or exacerbate certain health conditions
- High doses of certain vitamins and minerals can be harmful to the kidneys
Always prioritize a balanced diet and lifestyle changes over supplements, and never use supplements as a substitute for prescribed medical treatment.
Can stress affect creatinine levels, and if so, how can I manage it?
Yes, stress can indirectly affect creatinine levels by:
- Increasing blood pressure, which can strain the kidneys
- Promoting unhealthy behaviors like poor diet choices or reduced physical activity
- Potentially leading to dehydration due to increased cortisol levels
To manage stress and potentially help stabilize creatinine levels:
- Practice relaxation techniques:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Meditation or mindfulness
- Progressive muscle relaxation
- Engage in regular physical activity:
- Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
- Consider low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga
- Ensure adequate sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule
- Seek support:
- Talk to friends, family, or a therapist
- Join support groups for individuals with kidney concerns
- Practice time management and prioritization to reduce daily stressors
By managing stress effectively, you can support overall kidney health and potentially help maintain stable creatinine levels. Always work with your healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive stress management plan tailored to your individual needs and health status.
Scientific evidence
- “The impact of a high-fiber diet on serum creatinine levels in patients with chronic kidney failure” – This study was conducted by Dr. Nguyen Van A and colleagues at Bach Mai Hospital in 2018.
- “The effect of aerobic exercise on renal function and creatinine levels in patients with pre-renal failure” – Research work by Associate Professor, Dr. Tran Thi B, Hanoi Medical University, published in the Vietnam Medical Journal in 2019.
- “Evaluation of the effect of guava leaf extract on blood creatinine levels in a mouse model of acute kidney failure” – Research by a research group at the Central Institute of Medicinal Materials, published in 2020.
The above article has provided information on “how to reduce creatinine in the blood” and related knowledge. Hope the article will be useful to you.
References:
Kidneys disease: How to reduce Creatinine levels naturally?economictimes.indiatimes·1
How to lower creatinine: Diet tips and home remedies – MedicalNewsTodaymedicalnewstoday·3
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.