Swollen lower molar gums occur when the gum tissue around the lower molar becomes inflamed and swollen, accompanied by pain and various other uncomfortable symptoms. This condition not only affects daily chewing activities but also poses the risk of dangerous complications. Let’s explore the causes, treatments, and prevention of “swollen lower molar gums” in this article.
Causes of Swollen Lower Molar Gums
There are many potential causes of “swollen lower molar gums” with the most common being:
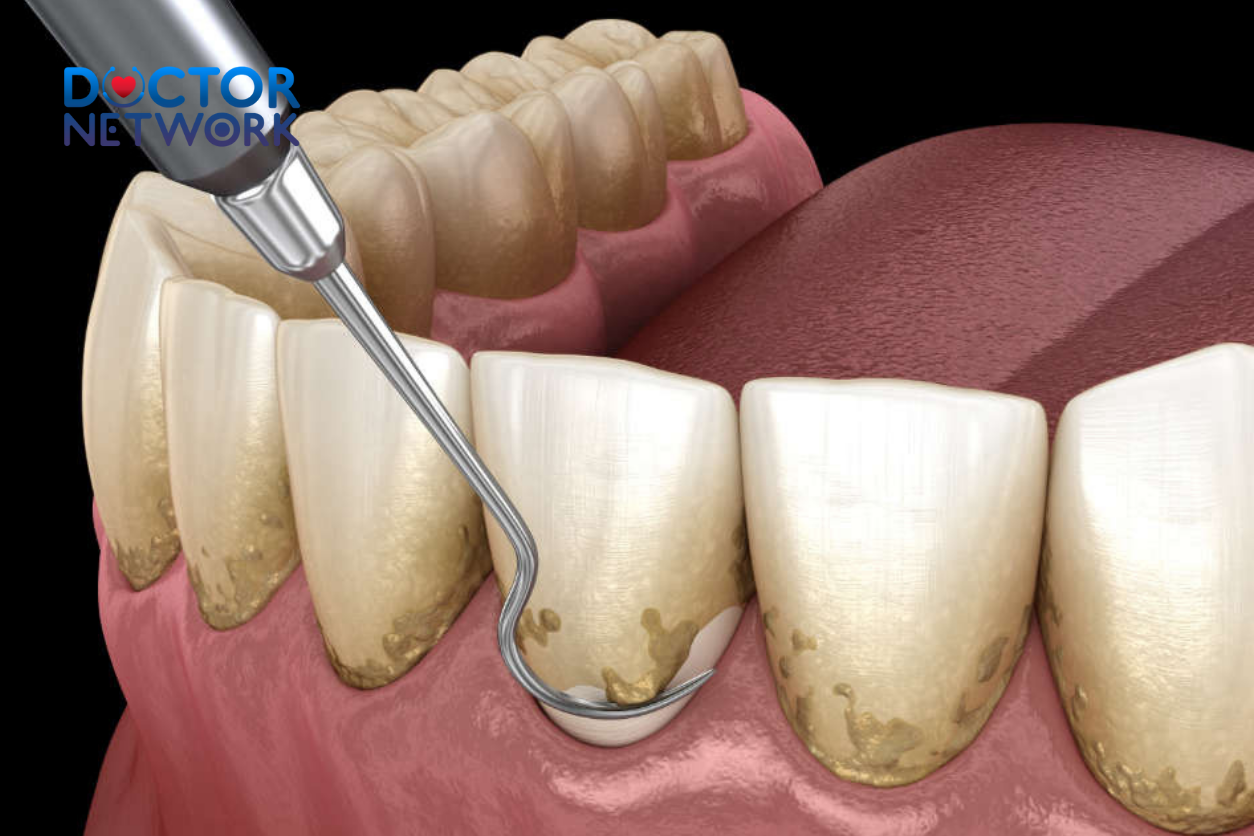
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Bacteria in food debris accumulated on the tooth surface for a long time is the main cause of inflammation, damaging the gum tissue around the tooth root.
Bacteria in food debris accumulated on the tooth surface for a long time is the main cause of inflammation
- Periodontitis: This condition occurs when gingivitis is left untreated, leading to severe inflammation and destruction of the structures supporting the teeth (alveolar bone, periodontal ligaments), causing swelling and pain in the gums.
- Tooth Decay: When tooth decay progresses severely, bacteria can invade the tooth pulp and root area, causing inflammation and swelling of the lower molar gums.

When tooth decay progresses severely causing inflammation and swelling of the lower molar gums
- Wisdom Teeth Eruption: Misaligned or impacted wisdom teeth can push against adjacent teeth or damage the surrounding gums due to insufficient space to grow straight, causing gum swelling.
- Other Causes: Tooth abscess (infection around the tooth root), trauma, allergic reactions to some toothpaste or mouthwash ingredients, etc.
Accompanying Symptoms
Besides “swollen lower molar gums” patients may experience other symptoms such as:
- Pain: The pain can be dull or severe, increasing when chewing or when pressure is applied to the affected tooth area.
- Red, Swollen Gums: Inflamed gums appear dark red and bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
- Bad Breath: Originates from the infection site in the mouth.
- Systemic Symptoms: In cases of widespread infection, patients may have a mild fever and swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
Diagnosis of Swollen Lower Molar Gums
To diagnose “swollen lower molar gums” the dentist will:
- Clinical Examination: Carefully observe and examine to identify the damaged tooth, the location and extent of the swelling, and assess the condition of the gums and surrounding structures.
- Dental X-rays: X-ray images provide detailed information about the internal structure of the teeth and alveolar bone, helping to evaluate the extent of damage and identify underlying causes.
Treatment of Swollen Lower Molar Gums
The goal of treating “swollen lower molar gums” is to eliminate the cause and control the symptoms. Depending on the severity and cause of the condition, the dentist will advise on appropriate treatment options:
Treating the Cause of Swollen Lower Molar Gums:
- Professional Oral Hygiene: Removing tartar and cleaning plaque to eliminate bacterial infection, reducing inflammation.
- Treating Tooth Decay and Pulpitis: Removing infected tissue, filling cavities, or performing root canal treatment.
- Treating Periodontitis: Scaling and root planing combined with antibiotics (if necessary).
- Extracting Wisdom Teeth: In cases where misaligned or impacted wisdom teeth cause complications.
Symptom Relief:
- Saline Mouthwash: Diluted saltwater helps reduce inflammation and disinfect. Rinse 2-3 times a day.
- Cold Compress: Helps reduce temporary swelling and pain.
- Medication: Doctors may prescribe pain relievers, antipyretics, and anti-inflammatory drugs in some cases.

Doctors may prescribe pain relievers, antipyretics, and anti-inflammatory drugs in some cases
Preventing Swollen Lower Molar Gums
To reduce the risk of swollen lower molar gums, you should:
- Maintain Thorough Oral Hygiene:
- Brush teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss to clean between teeth.
- Use antibacterial mouthwash.
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Visit the dentist every six months for screenings, early detection, and treatment of oral problems.
- Healthy Diet: Limit foods high in sugar and starch.
Precautions for Swollen Lower Molar Gums
- Should: Visit the dentist for timely examination and treatment.
- Should Not: Self-treat at home, apply heat, or press on the swollen area. This can worsen the infection.
Frequently Asked Questions About Swollen Lower Molar Gums
Question 1: Are swollen lower molar gums dangerous?
Answer: Swollen lower molar gums are usually not too serious if caused by poor oral hygiene or mild gingivitis. However, if left untreated, the infection can spread, leading to more severe complications such as:
- Tooth abscess
- Jawbone osteomyelitis
- Blood infection (in very rare cases)
It is best to see a dentist when you notice signs of swollen gums.
Question 2: How long does it take for swollen lower molar gums to heal?
Answer: Recovery time depends on the cause and treatment method:
- If due to poor oral hygiene or mild gingivitis: swelling may reduce in a few days with thorough cleaning and saline mouthwash.
- If due to tooth decay, periodontitis, impacted wisdom teeth: treating the dental issue may take several weeks or even months.
Question 3: Can swollen lower molar gums heal on their own?
Answer: In some mild cases, careful home care can improve the swelling. However, most cases only see temporary symptom relief without addressing the root cause. Without dental treatment, the infection will progress, causing further complications.
Question 4: What should I eat and avoid when having swollen lower molar gums?
Answer:
- Eat: Soft, easy-to-chew foods like soup, porridge, yogurt, and well-cooked dishes. Cool or room temperature foods to avoid irritating the swollen area.
- Avoid: Hard, chewy foods that require excessive chewing effort. Very hot or cold foods. Sugary foods, sweets, and carbonated drinks.
Question 5: Do I need to extract wisdom teeth if they cause gum swelling?
Answer: Not all cases of gum swelling due to wisdom teeth require extraction. The dentist will assess the extent of impaction and complications, then provide appropriate recommendations. In many cases, after the inflammation subsides, wisdom teeth may grow normally without causing problems.
Scientific Evidence on Swollen Lower Molar Gums
- A study in the “Journal of Clinical Periodontology” (2015) shows that plaque is the main risk factor for gingivitis and periodontitis, leading to swollen gums.
- The “American Academy of Periodontology” states that periodontitis is the most common cause of swollen gums, affecting 47% of adults aged 30 and over.
- According to the “World Health Organization,” tooth decay is the most common disease worldwide, affecting 60% of children and 90% of adults.
“Swollen lower molar gums” is a warning sign of dental problems. To protect your oral health and prevent complications, maintain thorough oral hygiene habits, have regular dental check-ups, and seek timely medical intervention when you notice any abnormalities.
References:
Kiểm Duyệt Nội Dung
More than 10 years of marketing communications experience in the medical and health field.
Successfully deployed marketing communication activities, content development and social networking channels for hospital partners, clinics, doctors and medical professionals across the country.
More than 6 years of experience in organizing and producing leading prestigious medical programs in Vietnam, in collaboration with Ho Chi Minh City Television (HTV). Typical programs include Nhật Ký Blouse Trắng, Bác Sĩ Nói Gì, Alo Bác Sĩ Nghe, Nhật Ký Hạnh Phúc, Vui Khỏe Cùng Con, Bác Sỹ Mẹ, v.v.
Comprehensive cooperation with hundreds of hospitals and clinics, thousands of doctors and medical experts to join hands in building a medical content and service platform on the Doctor Network application.